Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Info About Is RCCB Better Than RCD
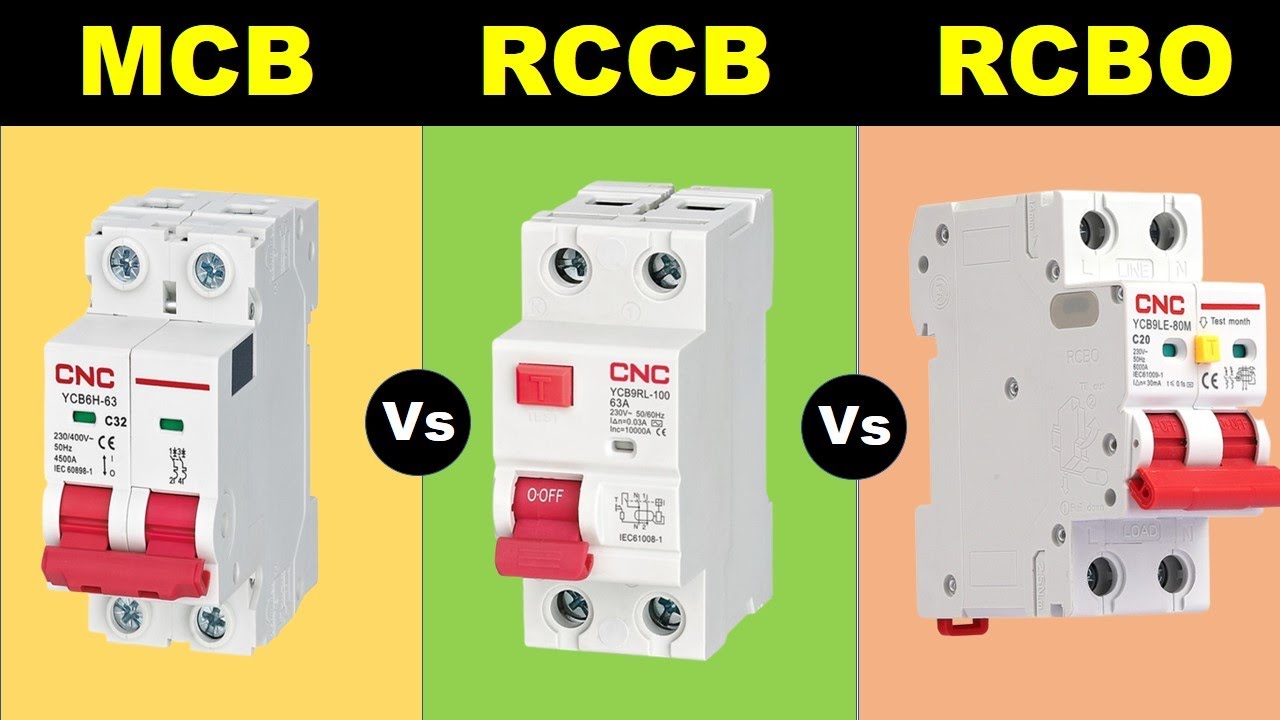
Difference Between MCB, MCCB, RCB And RCBO, 50 OFF
RCCB vs. RCD
1. Understanding the Core Function
Okay, let's talk about electricity — not the most thrilling subject, I know, but bear with me. We're diving into the world of safety devices designed to protect you from nasty shocks. You've probably heard of RCDs (Residual Current Devices) and RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers), and you might be wondering, "Are they the same thing? Is one better than the other?" It's a common question, and the answer involves a little electrical engineering, but I'll keep it simple, promise!
Think of these devices as vigilant guardians, constantly monitoring the flow of electricity in your circuits. Their primary job is to detect any leakage current, that sneaky electricity that's escaping where it shouldn't be. This leakage could be due to faulty wiring, damaged appliances, or, you guessed it, someone accidentally touching a live wire (yikes!). The moment these guardians sense something amiss, they trip the circuit, cutting off the power supply and preventing a potentially fatal electric shock.
So, why the two different names, RCD and RCCB? Are they interchangeable terms? Not exactly. While they share the same fundamental purpose — protecting against electric shock — there are subtle but important distinctions between them. It's like the difference between a general practitioner and a specialist; both are doctors, but one has a broader scope while the other focuses on a specific area.
Imagine your electrical system as a body. Both RCDs and RCCBs are there to protect it from harm. Now, let's get into the specifics and see where they differ and if one truly reigns supreme.

Delving Deeper
2. The Nitty-Gritty Details (Without Getting Too Nitty-Gritty)
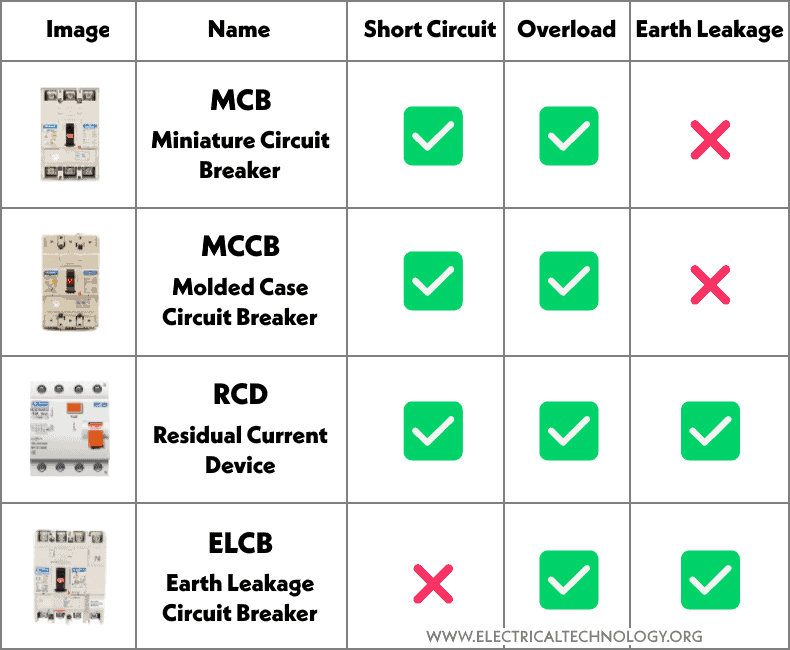
Right, let's get a little more technical, but I promise to keep it digestible. An RCD, in its broadest sense, is the umbrella term for any device that monitors residual current and trips a circuit when an imbalance is detected. This includes devices like RCCBs, RCBOs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers with Overcurrent Protection), and even some older types of earth leakage circuit breakers (ELCBs).
An RCCB, on the other hand, is a specific type of RCD. It's designed to detect residual current and trip the circuit, but it doesn't offer any protection against overcurrent or short circuits. That's where circuit breakers (MCBs) come in. Think of the RCCB as a specialized tool in the electrician's toolbox, focusing solely on residual current protection. It's a highly sensitive device, designed to react quickly to even small leakage currents.
The key difference, and this is crucial, is that an RCCB only protects against earth leakage (residual current). It won't trip if there's an overload (too much current being drawn) or a short circuit (a direct connection between live and neutral). Therefore, an RCCB needs to be used in conjunction with a separate circuit breaker (MCB) that provides overcurrent and short-circuit protection. They work as a team!
So, in essence, all RCCBs are RCDs, but not all RCDs are RCCBs. Confused? Don't worry, many people are! Just remember that RCD is the general category, and RCCB is a specific type within that category. It's like squares and rectangles. All squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares. And just like squares need a friend in case they get lonely, RCCBs always need an MCB for backup.

Protection Power-Up
3. Beyond Just Tripping the Switch
Let's talk about the different types of protection each device gives us. As we mentioned, the RCCB is a champion at protecting against earth leakage. This type of fault is particularly dangerous because it can lead to electric shock. The RCCB's sensitivity means it can trip very quickly, often within milliseconds, minimizing the duration and severity of any potential shock. It's like having a super-fast reflex!
However, the RCCB is not designed to handle overloads or short circuits. An overload happens when you draw too much current through a circuit, for example, by plugging too many appliances into a single outlet. A short circuit, on the other hand, is a more dramatic event — a direct connection between live and neutral, resulting in a sudden surge of current. In these situations, the RCCB won't trip, and that's where the MCB (miniature circuit breaker) comes in to save the day.
The MCB is specifically designed to protect against overcurrent and short circuits. It monitors the current flowing through the circuit, and if it exceeds a certain threshold, it trips, cutting off the power supply. This prevents damage to your wiring, appliances, and potentially even fires. The MCB and RCCB are the dynamic duo of electrical safety, working together to provide comprehensive protection.
Think of it this way: the RCCB is like a smoke detector, alerting you to a potential fire (earth leakage) before it starts. The MCB is like a sprinkler system, automatically extinguishing the fire (overcurrent or short circuit) if it does break out. Both are essential for a safe and secure home.

The Verdict
4. It's Not a Competition, It's a Team Effort!
So, is RCCB "better" than RCD? The short answer is: it depends on what you mean by "better." The slightly longer answer is: it's not really a question of which is better, but rather which is the right tool for the job. An RCCB is a specific type of RCD designed for a specific purpose: earth leakage protection. It excels at this, but it doesn't provide complete protection on its own.
You can't simply replace all RCDs with RCCBs and expect to have a safer electrical system. In fact, doing so could actually make your system less safe if you're not also providing overcurrent and short-circuit protection with MCBs. The key is to understand the different types of protection required for your specific electrical installation and to choose the appropriate devices accordingly.
The best approach is to use a combination of RCDs and MCBs to provide comprehensive protection against all types of electrical faults. This might involve using an RCCB in conjunction with an MCB, or it might involve using an RCBO, which combines the functions of both devices in a single unit. The choice depends on factors such as the size of your installation, the types of circuits involved, and your local electrical regulations.
Instead of thinking about which is "better," think about which combination provides the most complete protection. It's like asking whether a hammer is "better" than a screwdriver — it depends on whether you're trying to drive a nail or screw. The same principle applies to electrical safety devices: choose the right tools for the job, and make sure they're working together effectively.
Practical Applications and Installation
5. Putting Theory into Practice
Okay, enough with the theory, let's get practical! Where are RCCBs commonly used? You'll often find them in consumer units (fuse boxes) protecting circuits that supply power to areas where there's a higher risk of electric shock, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas. They're also commonly used in industrial settings to protect machinery and equipment.
When it comes to installation, it's crucial to remember that working with electricity can be dangerous. Always consult a qualified electrician for any electrical work, including the installation of RCDs, RCCBs, or MCBs. They'll be able to assess your specific needs, choose the appropriate devices, and ensure that everything is installed correctly and safely.
A qualified electrician will also perform regular testing of your RCDs and RCCBs to ensure that they're functioning properly. This typically involves using a specialized tester to simulate an earth leakage fault and verifying that the device trips within the specified time. Regular testing is essential to ensure that your safety devices are always ready to protect you when you need them most. It's like giving your electrical safety system a regular health check-up!
So, remember, electricity is powerful and potentially dangerous. Don't take any chances when it comes to safety. Consult a qualified electrician for all your electrical needs, and make sure your RCDs and RCCBs are properly installed and regularly tested.
