Favorite Info About How Many Volts Is Delta

Electric Basic Knowledge Atelieryuwa.ciao.jp
Understanding Delta Voltage
1. Decoding Delta Connections
So, you're diving into the world of electrical systems and stumbled upon "Delta." Good for you! It's a fundamental concept, especially when dealing with three-phase power. But what exactly does "How many volts is Delta" mean? Well, it's not about a fixed number. Delta refers to a specific type of electrical circuit connection, not a voltage itself. Think of it like asking, "How many miles per hour is a sedan?" It depends on the specific car and how hard you're pressing the gas pedal, right? Similarly, the voltage in a Delta system depends on the design of the system.
Instead of a single answer, we need to talk about how Delta connections work and how voltage fits into the picture. Imagine three electrical phases connected in a triangle (that's where the "Delta" name comes from, it looks like the Greek letter Delta Δ). In a Delta configuration, the voltage measured across any two of these points (or "lines") is the line voltage. And the voltage across each individual winding (the triangle's sides) is the phase voltage. The key difference in a Delta setup is that the line voltage and phase voltage are the same.
Now, let's put some real-world numbers into the mix. A very common Delta voltage level is 480 volts. This means you'd measure 480 volts between any two of the three lines coming from a 480V Delta system. Another common voltage is 240 volts. These are just examples; the actual voltage depends on the specific equipment and application. To know the exact voltage, you'll need to check the equipment's nameplate or consult the system's documentation. It's crucial for safety and proper operation!
Think of a Delta connection like a team of three strong friends pulling a load. Each friend (phase) contributes, and the overall pull (voltage) is the combined effort. If one friend isn't pulling their weight, the whole system suffers. That's why balanced voltage is so vital in Delta systems. An imbalance can lead to overheating, equipment damage, and inefficiency. So, "How many volts is Delta?" It's not a trick question, just one that requires a deeper understanding of how three-phase power works.

Volts, Amps, And Watts Explained OUPES Beginner's Guide 2 YouTube
Why Delta Connections are Used
2. The Advantages of Delta Configurations
Okay, so we know Delta connections are a thing, but why use them in the first place? What makes them the preferred choice in certain electrical setups? Well, Delta configurations have some advantages that make them well-suited for specific applications. One significant benefit is their ability to handle unbalanced loads more effectively than some other connection types. What does that mean?
Imagine a factory with a variety of equipment running at different times — some drawing a lot of power, others drawing very little. This creates an unbalanced load. Delta connections can "absorb" some of this imbalance, preventing voltage fluctuations and ensuring a more stable power supply. It's like having a suspension system in your car that smooths out the bumps in the road. Delta connections help to smooth out the "bumps" in power demand.
Another advantage is the availability of a "high leg" or "wild leg" in some Delta configurations. This is a single-phase voltage that's higher than the other two. This can be useful for powering certain types of equipment that require a higher voltage. However, it's important to note that this high leg can also be a safety hazard if not properly identified and handled. Think of it like a hidden trapdoor; you need to know it's there and how to avoid falling in!
Delta connections also have a built-in redundancy. If one phase fails, the system can often continue to operate at a reduced capacity. It's like having a backup engine in an airplane. It's not ideal, but it can keep you going until you can get the problem fixed. While it's not recommended to run indefinitely on a single phase, it can provide valuable time to switch to a backup system or safely shut down operations. In short, Delta connections offer a balance of performance, reliability, and flexibility, making them a valuable tool in the electrical engineer's toolbox.

Difference Between Star And Delta Connections YouTube
Delta vs. Wye (Star) Connections
3. Understanding the Differences
Now that we've spent some time exploring Delta connections, it's essential to compare them to another common type: Wye (also known as Star) connections. Understanding the differences between these two configurations is crucial for choosing the right one for a particular application. They both serve the purpose of distributing three-phase power, but they do so in different ways, leading to distinct advantages and disadvantages.
The key difference lies in how the phases are connected. In a Delta connection, the phases are connected in a closed loop, forming a triangle. In a Wye connection, the phases are connected to a common neutral point, forming a "Y" shape. This neutral point provides a return path for current, which is essential for single-phase loads. Think of it like a road system: Delta is like a roundabout, while Wye is like a highway with an exit ramp.
As mentioned before, Delta connections have line voltage equal to phase voltage. But in Wye connections, the line voltage is √3 (approximately 1.732) times the phase voltage. This means that for the same phase voltage, a Wye connection will have a higher line voltage than a Delta connection. This difference in voltage characteristics makes Wye connections well-suited for long-distance power transmission, as the higher voltage reduces current and minimizes losses.
Wye connections also offer the advantage of providing both three-phase and single-phase power from the same system. This is because the neutral point allows for connecting single-phase loads between each phase and neutral. Delta connections, on the other hand, typically only provide three-phase power unless a center-tapped transformer is used. So, Delta is great for powering large industrial motors, while Wye is more versatile for a wider range of applications. Choosing between Delta and Wye depends on the specific needs of the electrical system, considering factors such as load balancing, voltage requirements, and the need for single-phase power.
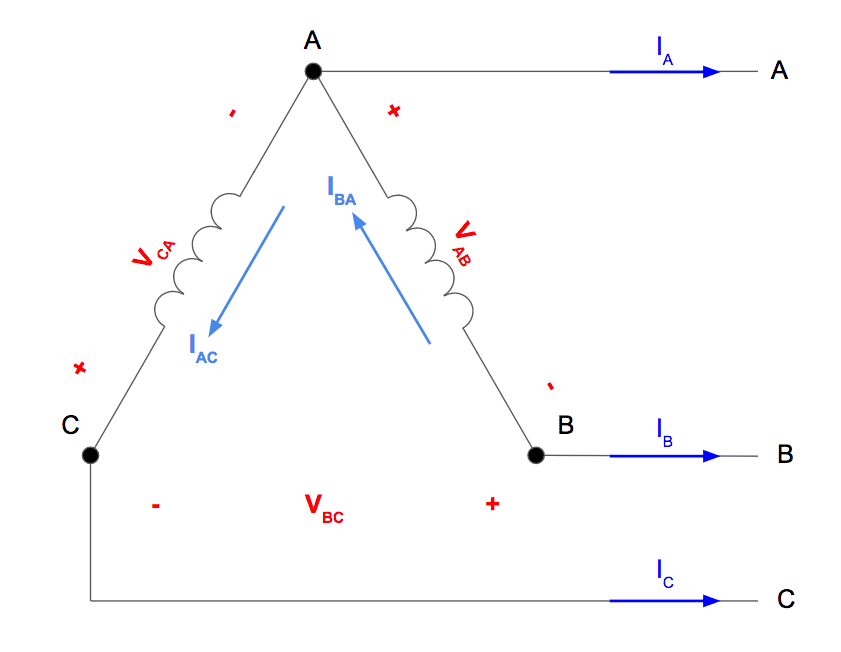
Delta Diagram
Safety Considerations with Delta Systems
4. Handling Delta Power Responsibly
Alright, let's talk safety. Working with electrical systems, especially Delta configurations, demands respect and a thorough understanding of potential hazards. Electricity is powerful and unforgiving, so it's vital to take precautions to protect yourself and others. Remember that high leg Delta we mentioned? That's one potential gotcha to be aware of!
The high leg, often marked with orange tape, can present a shock hazard if not properly identified. Because it has a higher voltage to ground than the other phases, it can easily overload and damage equipment that is not designed for this voltage. Always use a multimeter to verify the voltage between each phase and ground before connecting any equipment. Think of it like checking the water temperature before jumping into a pool; you want to avoid an unpleasant surprise!
Another important safety consideration is proper grounding. A properly grounded Delta system provides a path for fault current to flow back to the source, tripping the circuit breaker and preventing a dangerous buildup of voltage. This is like having a lightning rod on your house; it provides a safe path for the electricity to follow in case of a surge. Always ensure that the grounding system is properly installed and maintained.
Finally, never work on a live Delta system unless you are a qualified electrician and have the proper personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes insulated gloves, safety glasses, and arc-rated clothing. Always de-energize the system and verify that it is safe to work on before starting any repairs or maintenance. Think of it like rock climbing; you wouldn't attempt a climb without a harness and safety gear, right? Electrical work demands the same level of preparation and caution. By taking these safety precautions, you can help prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
Practical Applications of Delta Voltage
5. Where You'll Find Delta in the Real World
So, we've covered the theory and the safety aspects, but where does Delta voltage actually show up in the real world? What types of equipment and industries rely on Delta connections for their power needs? Well, you'll find Delta systems in a variety of applications, particularly in industrial settings where high power loads are common.
One of the most common applications is powering large electric motors. These motors are used in everything from pumps and compressors to conveyor belts and machine tools. Delta connections are well-suited for these applications because they can provide the high starting torque required to get these motors moving. It's like having a powerful engine in a truck; it can haul heavy loads without bogging down.
Delta systems are also frequently used in distribution networks, especially for supplying power to commercial and industrial buildings. A Delta-Delta transformer configuration can step down the high-voltage power from the utility grid to a lower voltage suitable for use within the building. This allows for efficient power transmission and distribution. Think of it like a network of pipes delivering water to different parts of a city; the Delta system is like the main water lines that supply the buildings.
Another application is in welding equipment. Many industrial welders use Delta connections to provide the high current and voltage required for welding metal. The ability of Delta systems to handle unbalanced loads is also beneficial in welding applications, as the load can vary significantly depending on the welding process. So, the next time you see a welder in action, chances are it's being powered by a Delta system. In short, Delta voltage plays a crucial role in powering a wide range of industrial equipment and processes, making it an essential part of modern industry.
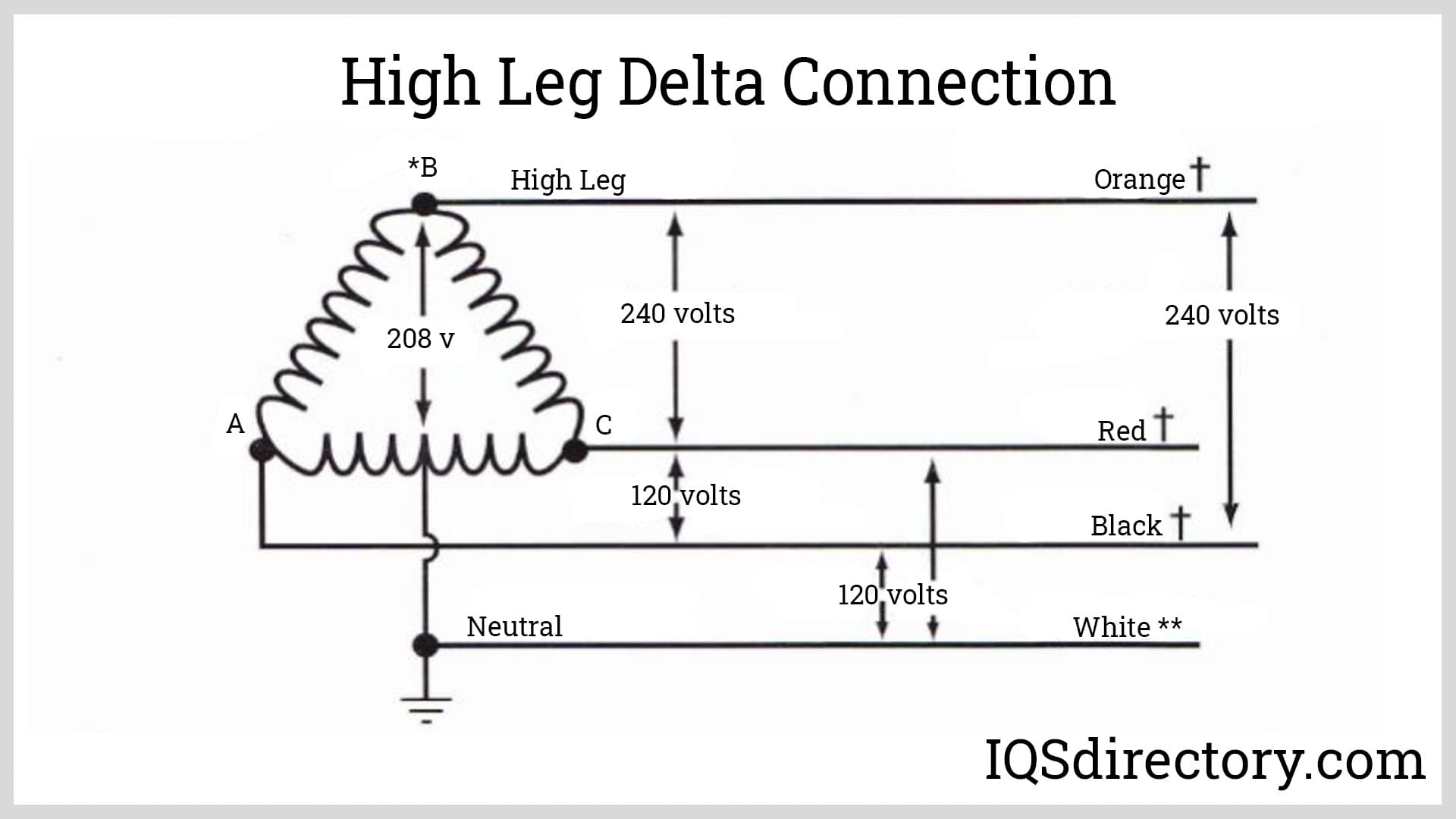
High Leg Delta Configurations
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still got questions about Delta voltage? No problem! Let's tackle some frequently asked questions to clear up any remaining confusion.
7. Q
A: If one phase fails, the system can often continue to operate at a reduced capacity, but it's not ideal. You'll experience a drop in power and potentially unbalanced voltages, which can damage equipment over time. It's best to address the issue quickly!
8. Q
A: While possible, it's not typical. Residential power is usually single-phase or Wye. Delta systems are more common in industrial settings. You'd need a special transformer to step down the voltage and convert it to a suitable form for household use. Is it practical? Usually not.
9. Q
A: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage between any two of the three lines. This will give you the line voltage, which is equal to the phase voltage in a Delta system. Always ensure the multimeter is set to the correct voltage range and use proper safety precautions!